By Adam Pagnucco.
Montgomery County’s giant tax hike will have consequences. Here are a few of them.
1. Term limits are more likely to pass.
There are several reasons why Robin Ficker’s newest term limits amendment will probably pass if he gathers enough signatures to place it on the ballot, but the tax hike is one of the biggest. The last time the council broke the charter limit in 2008, voters responded by passing Ficker’s charter amendment to make tax hikes harder. With a new tax hike in place, voters may be tempted to respond with term limits.
Ficker has taken notice. He regularly runs Facebook ads linking term limits, the tax hike and the council’s 2013 salary increase like the one below. Commenters respond predictably.
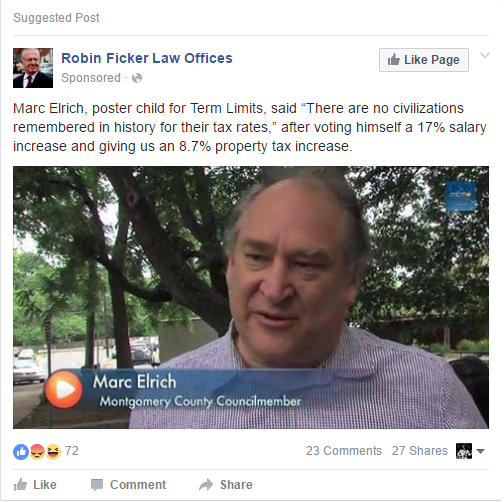
Ficker may have a new ally in his quest to evict the council: MCGEO President Gino Renne. After the council voted to abrogate his union’s collective bargaining agreement, Renne told the Post, “I’m tired of these clowns,” and said his union might support term limits. An alliance between Gino Renne and Robin Ficker would be one of the strangest events in the history of MoCo politics. Whoever can produce a picture of these two smiling and shaking hands will be awarded a gift certificate from Gino’s beloved Department of Liquor Control.
2. Outsider candidates could be encouraged to run for county office.
If term limits pass, two things will happen. First, the County Executive’s seat and five seats on the County Council will be open in 2018. Second, the tax increase will be blamed for the success of term limits. Both factors could lead to the entry of outsider candidates with a message like this: “We need new leadership. We need to do things differently.” Translation: we need to run the government without giant tax hikes.
Some of these outsiders may use the county’s new public financing system to run. But the strong performance of David Trone, who started with zero name recognition and won many parts of CD8, will encourage self-funders. This being Montgomery County, there are a LOT of potential self-funders, including those who have previously run for office. Candidates in public financing can raise as many individual contributions of up to $150 each as they are able to collect, but the system caps public match amounts at $750,000 for Executive candidates, $250,000 for at-large council candidates and $125,000 for district council candidates. A wealthy self-funder could easily overwhelm candidates who are subject to these caps and make a mockery of public financing.
3. More charter amendments on taxes are possible.
Ficker’s 2008 property tax charter amendment, which instituted the requirement that all nine Council Members must vote to override the charter limit on property taxes, was a mild version of his previous ballot questions on the subject. His 2004 Question A, which would have abolished the override provision entirely, failed by a 59-41 percent margin. Now that the 2008 amendment has been proven ineffective, Ficker could be encouraged to bring back his more draconian version soon. In the wake of this new tax hike, would voters support it?
Passage of a hard tax cap would have very grave consequences for the ability of county government to deal with downturns. In 2010, the County Council responded to the Great Recession by passing a tough budget combining cuts, furloughs, an energy tax increase and layoffs of 90 employees. When the next recession comes, if the county has no taxation flexibility, it might have to pass a budget laying off hundreds of people and gutting entire departments. If the levying of giant tax hikes in non-emergencies causes the voters to abolish the possibility of levying them in true emergencies in the future, it would be a serious calamity.
4. Governor Larry Hogan is a big winner.
One of Governor Hogan’s favorite political tactics is to play the Big Three Democratic jurisdictions against the rest of the state, with the City of Baltimore being his prime target. But he can also point to Prince George’s County, where the County Executive (and a potential election opponent) proposed a 15% property tax hike, and also to Montgomery County, where the council passed a 9% increase. His message to the voters will be a simple one.
“Look, folks. This is what you get when you allow liberal Democrats to have one-party rule: giant tax hikes. That’s why you need people like me in office to stop them.”
How many MoCo Democrats will ask themselves this question: “What is easier for me to live with? Larry Hogan or nine percent tax hikes?” What do you think their answer will be?
Hogan received 37% of the vote in Montgomery County in 2014. He had a 55% approval rating in MoCo according to a Washington Post poll last October. A Gonzales poll taken in March found that registered voters in the Washington suburbs (defined as MoCo, Prince George’s and Charles) gave Hogan a 62.6% job approval rating, with 35% strongly approving. If Hogan can use the tax issue to run in the low 40s, or even as high as 45% in MoCo, he will be very difficult to beat for reelection.
Reelecting himself is not Hogan’s only priority. He would also like to elect enough Republicans to the General Assembly to uphold his vetoes. That task is easier in the House of Delegates, where Democrats hold 91 seats, six more than the 85 votes required to override vetoes. If the GOP can pick up seven seats, as they did in 2014, they can uphold the Governor’s vetoes on party line votes. That would cause serious change in how Annapolis operates. Could big tax hikes in Democratic jurisdictions like Montgomery help the GOP get there?
5. It will be harder to get more aid from Annapolis.
In 2007, former Baltimore State Senator Barbara Hoffman commented to the Gazette on Montgomery County’s ultra-wealthy reputation in Annapolis. “They have to overcome the view that they’re rich and trouble-free. … That’s not true anymore.” She was right then, and she is even more right now. The county has massive needs for transportation projects and both operating and construction funds for the public schools. But when the county levies giant tax hikes on itself to pay for these needs, is it letting the state off the hook? State legislators from other cash-strapped jurisdictions that lack wealthy tax bases like Bethesda, Chevy Chase and Potomac are perfectly happy to let MoCo tax itself while they ask the state to tax MoCo even more to pay for their needs. (Remember the 2012 state income tax hike, of which MoCo residents paid 41% of the new revenue?) As a result, the next time the Lords of Annapolis are asked to help Montgomery County, they could very well reply, “Tax yourselves to pay for it. You always do.”
6. A major argument in favor of the liquor monopoly has been proven hollow.
County officials predicted that if the liquor monopoly was lost, annual property taxes would have to rise by an average $100 per household. Instead, the monopoly was preserved and the council passed a property tax hike that will cost an average $326 per household. The tax hike was in the works since at least January 2015, long before small businesses and consumers launched their campaign to End the Monopoly. And the $25 million in new spending added by the council to this year’s budget actually exceeds the $20.7 million that the liquor monopoly is projected to return to the general fund. This proves once and for all that liquor monopoly revenues do not prevent tax hikes!
7. There will be pressure in the future for another tax hike.
As we discussed in Part Three of this series, the U.S. Supreme Court’s Wynne decision, which requires counties to refund taxes paid on out-of-state income, was one reason for the current property tax hike. Senator Rich Madaleno’s state legislation extended the time that counties had to pay for refunds from Fiscal Year 2019 to 2024. Below is a table showing the fiscal impact on all Maryland counties combined, of which Montgomery accounts for roughly half. While the legislation enables counties to spend less in FY 2017-2018, it requires them to spend more in FY 2020-2024. MoCo will have to spend around $20 million a year in most of the out years.
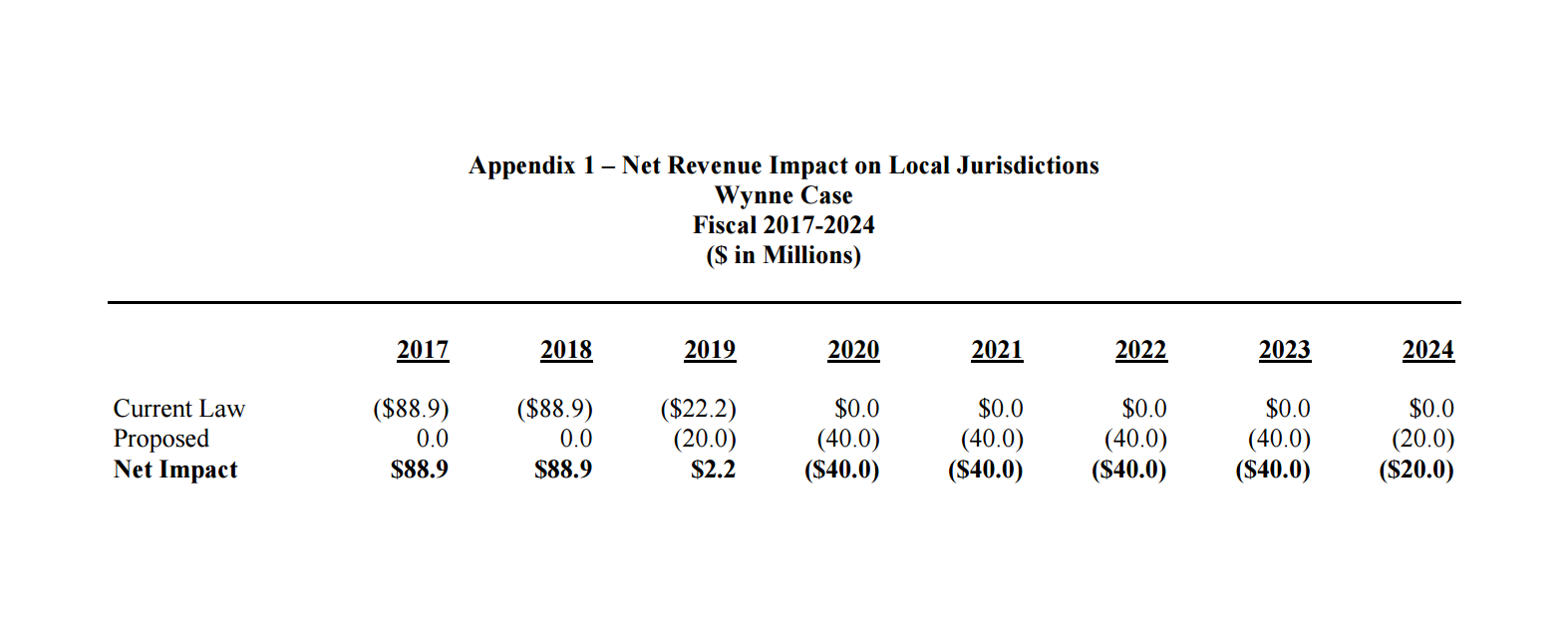
Given its $5 billion-plus annual budget, Montgomery could easily afford the out-year payments by slightly slowing the growth rate in its annual spending. But instead, the council added $25 million in new spending on top of the Executive’s FY 2017 budget, and unless it is cut, that spending will continue in future budgets. The cumulative impact of that new spending plus future Wynne refund payments will start to be felt in three years. At that point, the council could very well face a choice between trimming back their added spending or raising taxes. What do you think they will do?
8. Economic development will now be harder.
Despite the wealth in some of its communities, Montgomery County struggles with the perception that it is not business-friendly. While its unemployment rate is low by national standards, its real per capita income fell steeply during the recession, much of its office space is obsolete and it lacks Northern Virginia’s two major airports and its new Metro line. The chart below shows the county’s private sector employment from 2001 through 2014. Despite recent sluggish growth, the county had fewer private sector jobs in 2014 than it did in 2001.
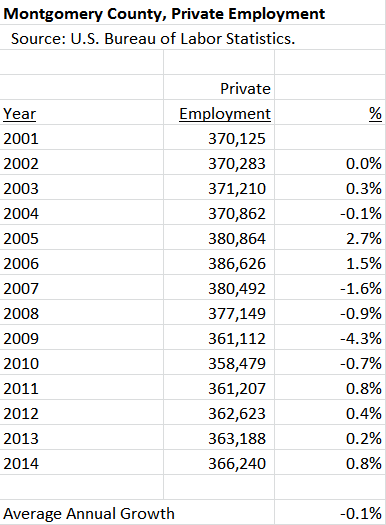
And while the county lost private sector jobs, the Washington region as a whole grew by 9.5% over this period.
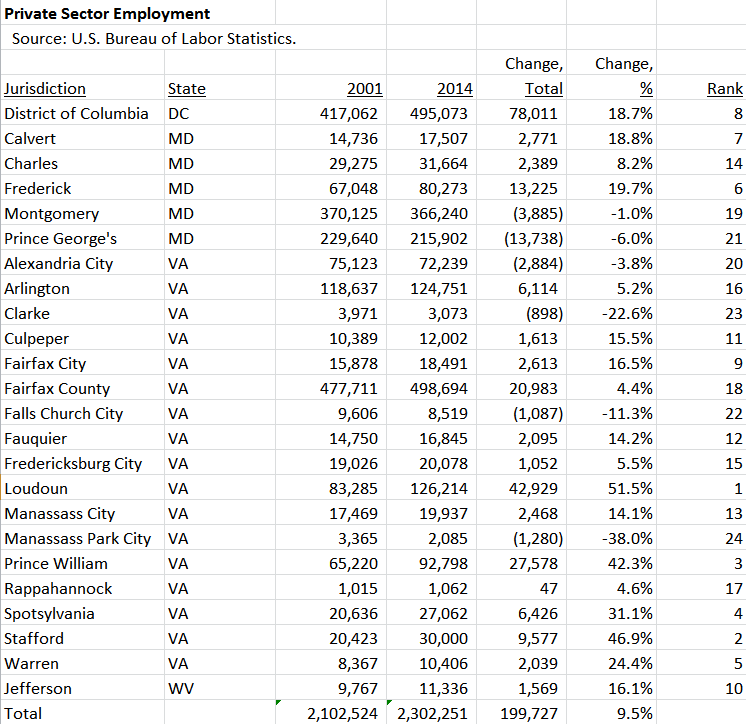
There may be a variety of factors explaining MoCo’s weak economic performance, but consider this: in the last 15 fiscal years, the county has seen six major tax increases. The county broke its charter limit on property taxes in FY 2003, 2004, 2005, 2009 and 2017 and it doubled the energy tax in FY 2011. (Most of the latter increase is still on the books.)
Good government is an exercise in balancing needs. Education, transportation, public safety and public services are valuable and require resources, at times necessitating tax increases. But all of that is impossible without a vigorous private sector that creates jobs and incomes and pays the government’s bills. Those priorities must be balanced, and when they are, progressive policies can be afforded. But if they are not, economic growth will fail, government services will be harder to sustain, taxes will fall increasingly on a shrinking base and a downward spiral could begin.
In the wake of its long-term stagnant economy and its Giant Tax Hike, how close is Montgomery County to that tipping point?