By Adam Pagnucco.
Make no mistake: running for school board is TOUGH. The MoCo school board has two at-large seats, five district seats and one seat elected by MCPS students. Of the seven non-student seats, all of them – at-large and district – are subject to voting by the entire county electorate. Three seats – one of the at-large seats plus Districts 2 and 4 – hold elections in presidential years, which attract tons more voters than gubernatorial years when elections for other state and county offices are held. Since the school board seats are non-partisan, both primaries and generals can be real competitions. Finally, Republicans, unaffiliated and third party voters can vote in school board primaries as well as generals. So school board candidates have to communicate with waaaaaay more voters than county-level and state legislative candidates and they have a lot less money to do that.
Dear readers, think about all of the above before you decide to run for school board!
And so these races are distinguished by little money, large electorates and woefully inadequate press attention. That’s why three factors are almost always key to deciding them. They are:
1. Incumbency. This is an important advantage in most elections. Incumbents have opportunities to learn the issues, assemble records, build relationships and accumulate name recognition. School board races are no exception.
2. The Apple Ballot. The Montgomery County Education Association (MCEA) has long had the most advanced political program of any group that participates in MoCo elections. Its centerpiece is the mighty Apple Ballot, an apple-shaped endorsement flyer that is widely distributed at election time. Few if any groups care more about school board elections than MCEA since board members set policy, hire the superintendent and approve collective bargaining agreements.

A version of the Apple Ballot from 2006. Note the placement of school board candidates at the top.
3. The Washington Post endorsement. The Post regularly endorses in school board races and the newspaper has a reach that extends beyond traditional Democratic voting constituencies. The Post is also occasionally critical of MCEA although it sometimes supports the same candidates as the teachers.
Without the benefit of significant resources to communicate with vast numbers of voters, school board candidates with one or more of the above advantages are heavily dependent on them to differentiate themselves from the pack. That’s why while all of the above advantages matter in any race, they may be especially critical to candidates for school board.
The table below shows candidates in contested school board races from 2006 through 2018 and the distribution of incumbency, the Apple Ballot and the Post endorsement. In some cases, the primary was uncontested because there were two or fewer candidates while the general was contested.
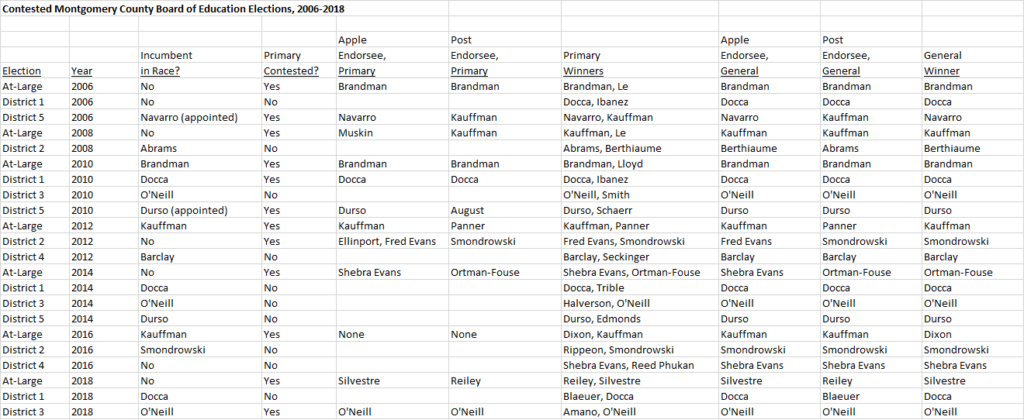
A casual glance demonstrates the value of incumbency, the Apple and the Post endorsement but let’s be more explicit. The table below shows win rates for all three, as well as combinations of some or all of them.

In every tabulation, candidates holding at least one of the above three advantages win at least 75% of the time. Holders of more than one advantage often win more than 90% of the time. Candidates holding both the Apple and the Post, whether or not they are incumbents, are nearly a lock. The one recent exception was in 2016, when at-large incumbent Phil Kauffman had both the Apple and the Post and was still defeated by former Paint Branch High School Principal Jeanette Dixon. In that race, Kauffman earned the Apple Ballot after the primary and the Post did not endorse him until October, possibly weakening the value of those endorsements.
These three factors don’t explain everything, but they explain a lot. While it’s possible to win without any of these advantages, as Dixon demonstrated, it’s very difficult. Keep an eye on these keys as this year’s school board races move forward.